|
Introduction
This study focuses on chitosan and chitin oligomers with a degree of polymerization (DP) below 10. These oligomers have beneficial effects on human health, as antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties. Studies have consequently shown the importance of these oligomers in many fields such as biomedical and agrochemical area.
Experimental conditions
The oligomers were analyzed using a system of size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). The separation was done on a series of two TSK gel G-Oligo-PW columns (7.8mm ID * 30cm L, 7μm). An aqueous solution of (NaCl 0.1M, pH=6) was employed as eluent. Differential refractometer (RI) was used as detection system.
Results
In these experimental conditions, the both oligomer series were found to be well separated in order of increasing molecular weight: large macromolecules are eluted first and the smaller ones are eluted after. This is explained by the fact that large macromolecules spend less time in the column because they do not enter into all the pores of the gel (contrary to small macromolecules).the chromatographic separation resolution of oligomer mixtures was satisfactory for DPs below 6.
Conclusion
This work allowed to be set up in an IMP laboratory a size-exclusion chromatography coupled with a differential refractometer detector. It was shown that this system can satisfactorily separate chitin and chitosan oligomers with low DP.
|
|
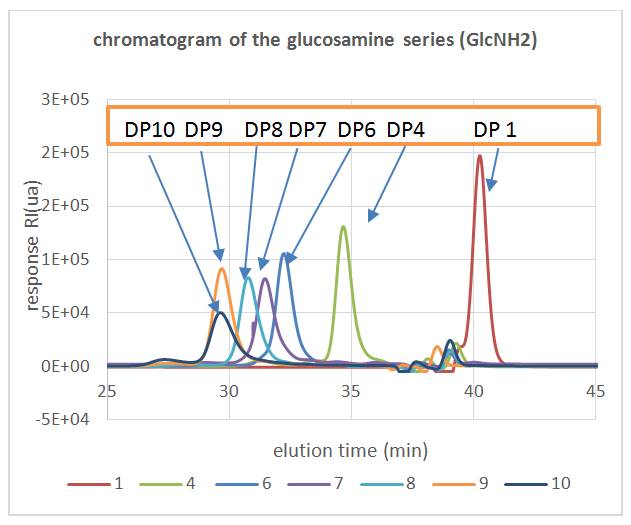
Example of an separation of glucosamine (Glc NH2) oligomers series: flow rate = 0.5ml/min, Injection volume = 100μl, RI detector, temperature = 25°C, 2 columns TSK gel G-Oligo-PW TOSOH (7.8mm ID * 30cm L, 7μm)
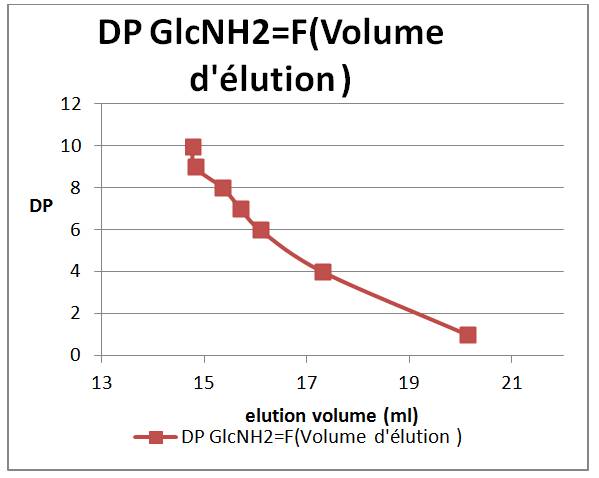
Evolution of elution volume as a function of degree of polymerization (DP)
|




