|
Introduction
VGC Chromatography (VGC) is a start-up company, founded in 2013, that manufactures gas chromatography (GC) columns. The acronym VGC stands for “Variable Geometry Column”, which is a new idea in GC column geometry. By creating a retention gradient along the column, they enable differential acceleration (DA), an improvement on differential migration that more efficiently uses time and column length.
This study focuses on columns that achieve DA by a stationary phase thickness gradient, the side that is connected to the inlet is the section with the thickest stationary phase and as it goes to the outlet the phase gets thinner.
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) method D2887, also known as simulated distillation (frequently abbreviated as SimDis or SimDist) is a method widely used in petroleum industries to characterize the boiling point range of petroleum fractions and products. SimDist was selected for this study because it is a demanding separation for any GC system but is also a large segment of the current GC column market.
Experimental conditions
ASTM D2887 standards were purchased from Spectrum Quality Standards. The standard is a 1 mL neat mixture of seventeen n-alkanes ranging from C644. The concentration of each compound varies from 1% to 12% (m/m). For these analyses, the mixture was diluted 100-fold (v/v) in carbon disulfide CS2.
The column used for this study featured polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) stationary phase (DA-1), 8 m x 0.250 mm, the film thickness varies from 200 nm to 0 nm.
Separation Conditions:
Platform: Agilent 7890
Injection: 1 μL, split 240:1 (7683b ALS)
Carrier gas: H2 (4 mL/min, constant flow)
Inlet: 350° C, Straight liner (2 mm ID) with glass wool
Temperature Program: 30° C for 0.5 min, 75° C/min to 250° C, 45° C/min to 115° C, 40° C/min to 175° C, 30° C/min to 250° C, hold 5 min
FID temperature: 350° C
H2 flow: 40 mL/min
Air flow: 400 mL/min
Constant Col + Makeup: 15 mL/min
Results
Neat alkane mixtures were used as diagnostic analyte mixtures (with very high split ratio) to optimize the separation conditions (flow rate, temperature program). The heating rate of the Agilent 7890 oven was a limiting factor, with faster heating, the analysis time could probably be further reduced. As it can be seen on the chromatogram obtained in figure 1, which shows the analysis of the ASTM D2887 standard, the elution time of the last alkane (C44) is under 7 min which is fast compared to what can be read in literature (usual timing is about 20 min). The first alkane (C6) partially co-elutes with the solvent CS2, which is not ideal, but tolerated in some D2887 methods. Improved C6 resolution can be achieved with a lower oven temperature or thicker stationary phase. The large tailed peak around 4 min was identified as contamination from the inlet split trap.
Conclusion
SimDis is a useful method in GC for quickly determining the boiling point range of petroleum fractions and products. Since it is becoming more frequently used in petroleum industries, GC column manufacturers are interested in technological advances that address this growing market. VGC Chromatography’s DA-columns enable fast SimDis analyses, which is valuable to the petroleum industry.
|
|
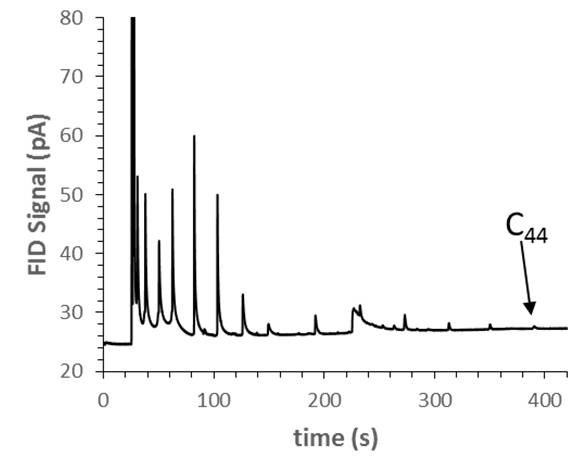
Chromatogram of ASTM D2887 calibration standard diluted 100x in CS2
|



