|
Introduction
Throughout the development of separation techniques, particle packed column with smaller particles was the first approach with the aim to obtain high efficient column and to reduce the analysis time but they are limited in pressure as the maximum pressure of conventional LC equipment is approximately 400 bars. To face this issue, ultra-pressure liquid chromatography UHPLC and HPLC were one of the solutions and a second approach was oriented towards monolithic stationary phases. Their greater permeability and low resistance to mass transfer allow working at a high speed without being restricted by pressure drop and to work with longer column to separate a maximum of compounds.
Adding miniaturized separation system enables synthesis of monolith in-situ in the capillaries leading to less problem of homogenous capillaries filling contrary to particle packed column. The miniaturization permits to reduce solvents and sample consumption such as biological or environmental sample which are very complex and sometimes in limited quantity. The bare silica monolith capillary synthesis by sol-gel process was optimized and their performance was tested in hydrophilic interaction HILIC by capillary electrophoresis CZE and by Nano-CPL.
Experimental conditions
Chromatographic studies of bare silica monolith column with short length were performed on Agilent Technology capillary electrophoresis equipped with a pressure limited to 12 bars, applied to the injection vial to introduce the sample into the capillary (injection on column) and a Diode Array detector (DAD). Data acquisition was collected by a 3D-CE Chemstation.
Chromatographic studies of bare silica monolith column with long length were performed on Eksigent NanoLC 400 equipped with a pumping system and a manual injector (injector loop: 10nL). For the detection, UV detector Actipix D100 was used and Data acquisition was treated by Azur.
A detection window was necessary and was created by burning the polyimide coating. The UV detection was carried out at 214nm. Silica monolith column was evaluated in HILIC with a mobile phase acetonitrile-water (95:5; v/v) and a mixture of naphthalene and nucleic compounds were respectively used as dead time and test solutes.
Results
For the morphological aspect, a scanning electron microscope was employed to determine the size of skeleton of the monolith and macropores and its anchor inside the capillaries.
Then different bare silica monolith columns were evaluated at an optimal linear velocity u=0.15cm/s in terms of retention, efficacy and permeability Ko.
Conclusion
These results show efficient and great permeability column and that’s why, HILIC recently gains a lot of interest for its broad range of applications such as polar compound separation, charged as well as uncharged and in multidimensional chromatography for its orthogonality proprieties with RP mode. This chromatographic mode could prove to be a promising tool in proteomics analysis and further research could be done with MS coupling.
|
|
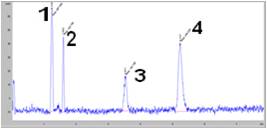
Electrochromatogram of nucleotides’ separation by CZE: (1) naphthalene (2) uridine (3) cytidine (4) cytosine
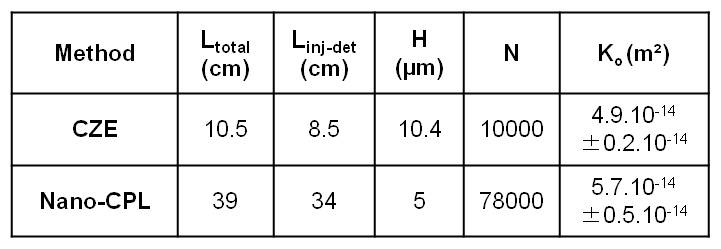
Recapitulative results of obtained efficacy, permeability on two silica monolith columns by 2 methods
|




