|
Introduction
Nowadays, the mass spectrometer is a « gold standard ». The automat Microflex LT/SH IVD MALDI Biotyper™ has a MALDI (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionisation) ionisation source and a TOF (Time Of Flight) analyser. It is used for bacterial and mycological identifications, thanks to the database that contains 5627 spectra of bacteria and yeasts.
The biological sample and the matrix are put on the MALDI target. There is co-crystallisation, then the laser brings its energy and a lot of ionized molecules are obtained: they are a proteins sequence of the bacterium or yeast. The spectrum of this sequence is compared to those from the database and a score between 0 and 3 is obtained.
The method is validated in line with ISO 15189:2012. This study has been realised with patient biological samples and ATCC (American Type Culture Collection) strains.
Experimental conditions
In line with ISO 15189:2012, contamination, robustness, accuracy and correlation of the methods (MALDI and Vitek 2 Compact Biomérieux) were verified.
• Robustness: capacity of the method to be not affected by small voluntary variations.
• Accuracy: measured by the analytic bias and inter-operator bias.
• Contamination: introduction, not intentionally, of an analyte in the sample.
Robustness
Tables for 6 ATCC bacteria and 2 ATCC yeasts and nearly 15 agars were made. Robustness was studied by using the culture age and the aerobic and anaerobic environment.
The method was judged robust.
Accuracy
Mean, standard deviation and RSD (Relative Standard Deviation) of 10 scores (repeatability) and 6 scores obtained by 3 operators (reproducibility) were evaluated. This was done with all ATCC strains. The goal was to have a mean higher than 2. The RSD was calculated to have an idea; in fact, the score was obtained with a biostatistic algorithm and didn’t have physical meaning. Generally, the RSD must be lower than 5%.
The method was judged accurate.
Contamination
Contamination problems weren’t met. Thus, the method was trustworthy.
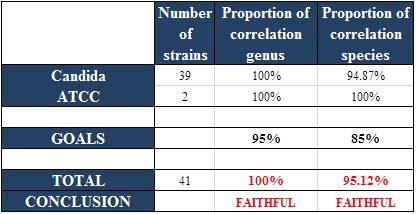
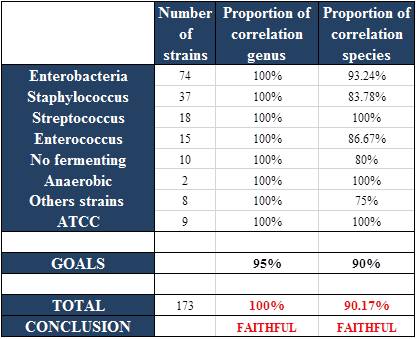
Correlation of methods
The method was judged reliable.
Results
At the end, limits of the technique were studied and a decision-making tree was established.
• It was uneasy to identify species constituted from many subspecies; such as Enterobacter (Enterobacter cloacae is a complex with a asburiae specie), Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas fulva belongs to the putida group), Citrobacter (Citrobacter freundii contains a braakii specie).
• Variability of operators and contamination of the strains can be a problem; such as staphylococcus negative coagulases.
• Limits of the database cause problems, because there are not enough spectra to discriminate many species (such as Achromobacter spp, Escherichia coli and Shigella, Streptococcus pneumoniae and oral).
Conclusion
The method was judged reliable. So it is used in lab since April to identificate bacteria and yeasts.
|
|
|



