|
Introduction
The Biology-Biochemistry laboratory of Bel-Air Hospital being in a process of accreditation, the validation of its methods is essential. The aim was the validation of the method of assaying vitamins A (retinol all-trans) and E (α-tocopherol) by HPLC-UV.
Experimental conditions
In order to quantify both vitamins A and E, an HPLC with UV detector was used. Operatory conditions are described below:
Column: Hypersil ODS 250mm*4.6mm*5µm
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 50µL
Mobile Phase: deionized water / methanol / ethanol
(5/82/13)
Detection: UV at 295 nm
Retention Times: 4.3 min (Vitamin A) and 13.6 min
(Vitamin E)
Samples were deproteinized to simplify the matrix and eliminate interferences.
Results
To perform this validation, many criteria such as linearity, repeatability, reproducibility and stability were tested.
On the one hand, linearity was assessed in the matrix (with ethanol) and showed the experimental results and the expected values were proportional. On the other hand, repeatability was checked by injecting a sample 20 times. Meanwhile, reproducibility was studied by injecting everyday a high and low control for 15 days. These parameters were validated by their coefficient of variation (CV) which must be less than the 10% set by the laboratory. (Fig 1 and 2).
Conclusion
The analytical method was partially validated. Indeed, some tests such as stability at -20°C for biological samples should be done again using this time a greater number of injections to reduce uncertainty. This will show if the degradation of the analyte on the fourth week was due to errors during sample preparation.
|
|
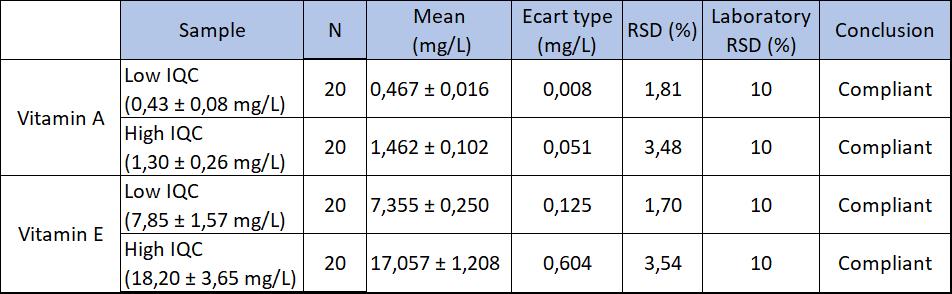
Fig 1: Results of repeatability (k=2, norm)
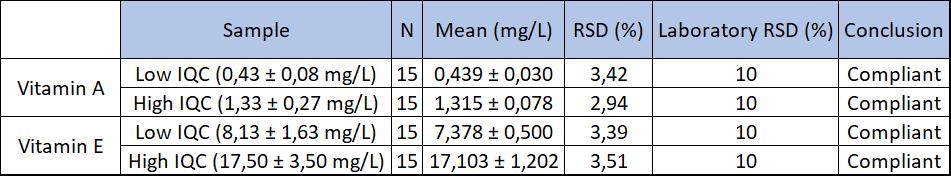
Fig 2: Results of reproducibility (k=2, norm)
|




