|
Introduction
The simultaneous analysis and quantification of small molecules at low concentrations levels in complex samples requires the use of a highly sensitive and specific detection system down-stream a separation step.
Thus, the coupling of liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry is the gold standard for such analysis. To ensure the reliability of the analysis, a full validation of the method has to be conducted. Such a validation was undertaken for the analysis of phenylureas by HPLC-ESI-TOF-MS. This validation was carried out according to NF T90 210 benchmark and relies on the study of the acceptable maximal distance (AMD).
Experimental conditions
The isocratic liquid chromatography separation was implemented in the reversed phase mode, with a Zorbax C18 2.1 mmi.d. x 50mm (pd = 1.8 µm) column and a 40/60 ACN/water mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.35 mL/min. The injection volume was 1.5 µL. The mass spectrometer system was a 6230 LC-TOF from Agilent Technologies. This mass spectrometer was equipped with an electrospray ionization source. Each solute was quantified by extracting the corresponding peak area at the m/z ration of the (M-H)+ adduct with a detection window fixed at 20 ppm.
The solutes (phenylureas) were prepared in deionized water at concentration ranging from 5 to 100 µg/L.
Validations experiments were carried out with a set of 8 pesticides according to NF T90-210 protocol including calibration curves, limits of quantification (LOQ) and yields studies.
Tests organization
The measurements used to build the calibration curves were performed for 5 days, by preparing 5 sets of calibration solutions at 5 concentration levels. Biases were calculated as follows:
Bias (%) = (x-y)/x *100
x : Concentration level (theoretical)
y : Concentration calculated with the calibration curve
Validation standard protocol assesses the validity of the calibration curves if the spray of the biases remains within an acceptable maximal distance (AMD) whose borders are modulated according to the laboratory directions.
Results
The biases of calculated concentrations were globally similar; around 30% bias for the LOQ level and less than 10% for other concentration levels. Spray of bias for peak areas at the LOQ level was higher but has a standard distribution due to the higher uncertainty percentage for low concentration levels.
Conclusion
As the selected AMDs for LOQ and other concentration levels were respectively 40% and 10%, the calibration curve study was validated.
|
|
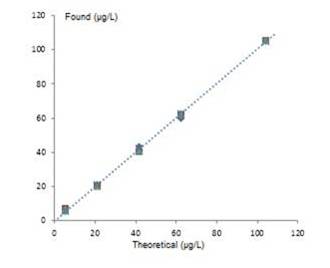
Calibration curve for the 5 levels of concentration for one of the pesticides
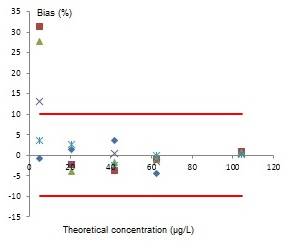
Biases observed for the 5 levels of concentration for one of the pesticides
|




